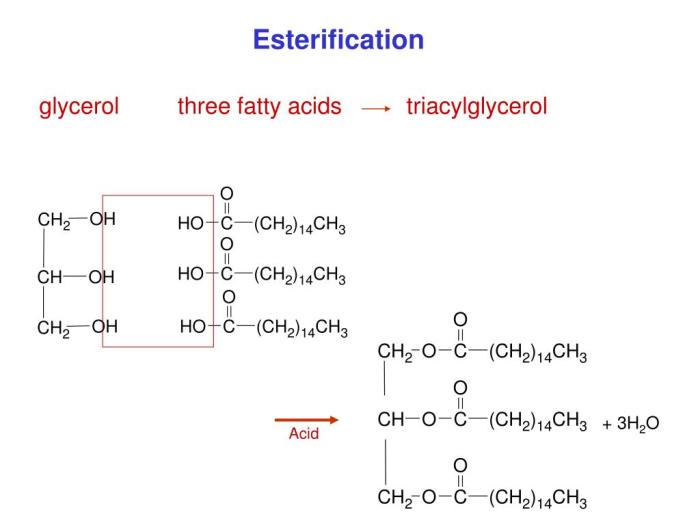
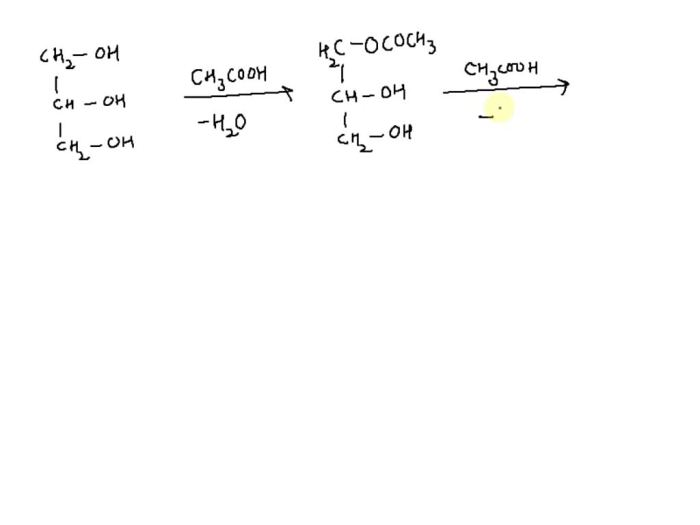
Esterification of glycerol and three ethanoic acids – Delving into the captivating realm of esterification, we embark on an in-depth investigation of the reaction between glycerol and three ethanoic acids. This intricate process unveils a symphony of chemical transformations, offering insights into the fundamental principles governing ester formation and its far-reaching applications.
As we unravel the intricacies of this reaction, we delve into the structural characteristics of glycerol and the three ethanoic acids involved, unraveling their molecular dance. The molar ratio between these reactants plays a crucial role in dictating the stoichiometry of the esterification process.
Esterification of Glycerol and Three Ethanoic Acids
Esterification is a chemical process that involves the reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid to form an ester. This reaction is commonly used in the production of various industrial and household products.
Esterification Reaction, Esterification of glycerol and three ethanoic acids
In an esterification reaction, the hydroxyl group (-OH) of an alcohol reacts with the carboxyl group (-COOH) of a carboxylic acid to form an ester (-COOR) and water. The general equation for this reaction is:
Alcohol + Carboxylic Acid → Ester + Water
The rate of esterification is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of reactants, temperature, and the presence of a catalyst.
Glycerol and Ethanoic Acids
Glycerol is a trihydric alcohol with the molecular formula C 3H 8O 3. It is a viscous, colorless liquid with a sweet taste.
The three ethanoic acids involved in the esterification are:
- Ethanoic acid (CH 3COOH)
- Propanoic acid (C 2H 5COOH)
- Butanoic acid (C 3H 7COOH)
The molar ratio of glycerol to ethanoic acids in this reaction is 1:3.
FAQ Summary: Esterification Of Glycerol And Three Ethanoic Acids
What is the significance of the molar ratio in the esterification of glycerol and ethanoic acids?
The molar ratio determines the stoichiometry of the reaction, ensuring the availability of reactants in appropriate proportions to achieve optimal esterification efficiency.
How does the reaction mechanism influence the rate of esterification?
The reaction mechanism involves a series of steps, including nucleophilic attack, proton transfer, and rearrangement. The rate of esterification is influenced by factors such as temperature, catalyst concentration, and the nature of the reactants.