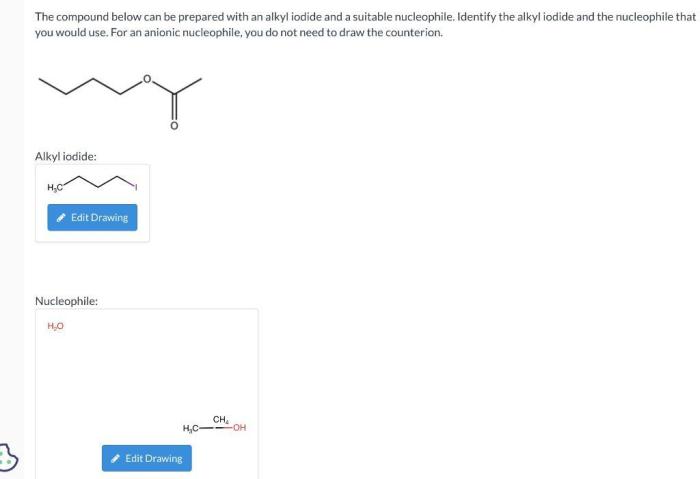
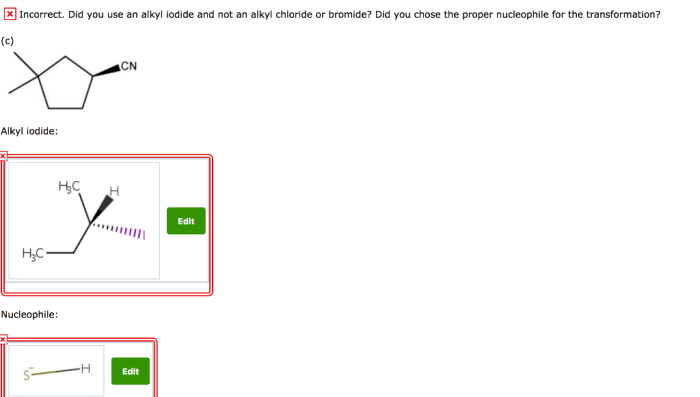
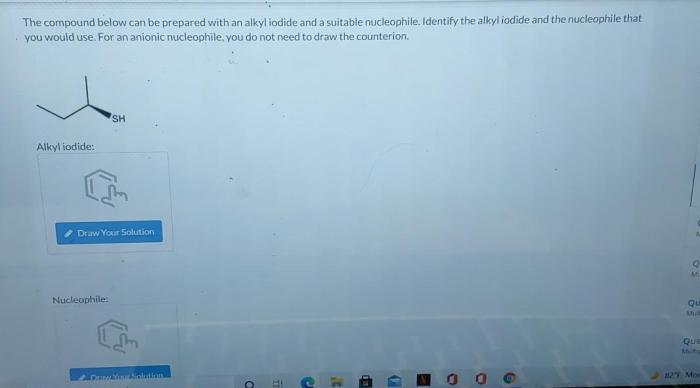
The compound below can be prepared with an alkyl iodide, a versatile synthetic intermediate employed in the construction of complex organic molecules. Alkyl iodides exhibit exceptional reactivity in substitution reactions, making them indispensable reagents for various transformations.
Their high reactivity stems from the weak carbon-iodine bond, which undergoes facile cleavage under mild reaction conditions. The choice of alkyl iodide, base, and solvent plays a crucial role in optimizing the reaction outcome.
Alkyl Iodide Reactivity
Alkyl iodides are highly reactive in substitution reactions due to the weak carbon-iodine bond, making them susceptible to nucleophilic attack. The reactivity is influenced by several factors:
- Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl iodides:Primary alkyl iodides are more reactive than secondary, and tertiary alkyl iodides are the most reactive due to steric hindrance.
- Nature of the nucleophile:Strong nucleophiles like alkoxides and amines react faster than weak nucleophiles like water.
- Solvent polarity:Polar solvents like dimethylformamide (DMF) enhance the reactivity of alkyl iodides by solvating the nucleophile and reducing its charge density.
Preparation of the Compound

The compound can be prepared using an alkyl iodide via a nucleophilic substitution reaction with a suitable nucleophile. The general mechanism involves:
- Nucleophilic attack:The nucleophile attacks the alkyl iodide, displacing the iodide ion.
- Formation of a tetrahedral intermediate:The nucleophile forms a bond with the carbon atom, creating a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Collapse of the intermediate:The iodide ion departs, resulting in the formation of the substituted product.
The base is used to deprotonate the nucleophile, increasing its nucleophilicity, while the solvent provides a suitable medium for the reaction.
Reaction Conditions
Optimizing the reaction conditions is crucial for maximizing product yield and selectivity:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures generally favor the reaction rate, but excessive heat can lead to side reactions.
- Time:Sufficient reaction time is necessary for complete conversion of the alkyl iodide.
- Solvent:The choice of solvent depends on the solubility of the reactants and the polarity required for the reaction.
Product Characterization
The product can be characterized using various analytical techniques:
- NMR spectroscopy:Provides information about the structure and connectivity of the atoms.
- IR spectroscopy:Identifies the presence of specific functional groups.
- Mass spectrometry:Determines the molecular weight and elemental composition.
Applications of the Compound, The compound below can be prepared with an alkyl iodide
The compound has potential applications in:
- Organic synthesis:As a starting material for the preparation of various organic compounds.
- Pharmaceuticals:As an intermediate in the synthesis of drugs and other pharmaceutical products.
- Materials science:As a precursor for the production of polymers and other materials.
Safety Considerations
Alkyl iodides are potentially hazardous and require proper handling:
- Toxicity:Alkyl iodides can be toxic if ingested or inhaled, so proper ventilation is essential.
- Reactivity:Alkyl iodides are reactive and can undergo exothermic reactions with strong oxidizers.
- Disposal:Alkyl iodides should be disposed of according to local regulations to prevent environmental contamination.
Essential FAQs: The Compound Below Can Be Prepared With An Alkyl Iodide
What are the advantages of using alkyl iodides in organic synthesis?
Alkyl iodides offer several advantages, including their high reactivity, which allows for efficient substitution reactions under mild conditions. They are also readily available and can be easily functionalized.
What factors influence the reactivity of alkyl iodides?
The reactivity of alkyl iodides is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the alkyl group, the solvent, and the base used in the reaction. Primary alkyl iodides are generally more reactive than secondary and tertiary alkyl iodides.
How can the reaction conditions be optimized for the preparation of the compound below using alkyl iodides?
Optimizing reaction conditions involves finding the ideal combination of temperature, time, and solvent to maximize product yield and selectivity. This can be achieved through experimentation and by understanding the factors that influence alkyl iodide reactivity.