Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive lymphatic system test questions and answers PDF. This invaluable resource delves into the intricate workings of the lymphatic system, providing a thorough understanding of its structure, function, and clinical significance.
Prepare yourself to master the complexities of the lymphatic system, unraveling its role in fluid drainage, immune responses, and overall health.
Lymphatic System Overview: Lymphatic System Test Questions And Answers Pdf
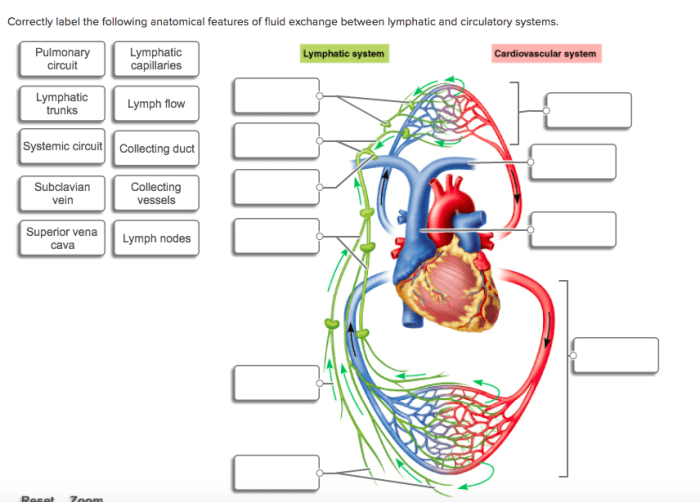
The lymphatic system is a complex network of vessels, nodes, and organs that work together to maintain fluid balance, remove waste products, and defend against infection.
Components of the lymphatic system include:
- Lymphatic vessels: Thin-walled vessels that collect and transport lymph fluid.
- Lymph nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph fluid and contain immune cells.
- Lymph: A clear fluid that contains white blood cells, proteins, and fats.
Functions of the lymphatic system include:
- Fluid balance: The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance by collecting excess fluid from tissues and returning it to the bloodstream.
- Waste removal: The lymphatic system removes waste products, such as cellular debris and toxins, from tissues and transports them to the lymph nodes for disposal.
- Immune defense: The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in the immune response by filtering out pathogens and activating immune cells to fight infection.
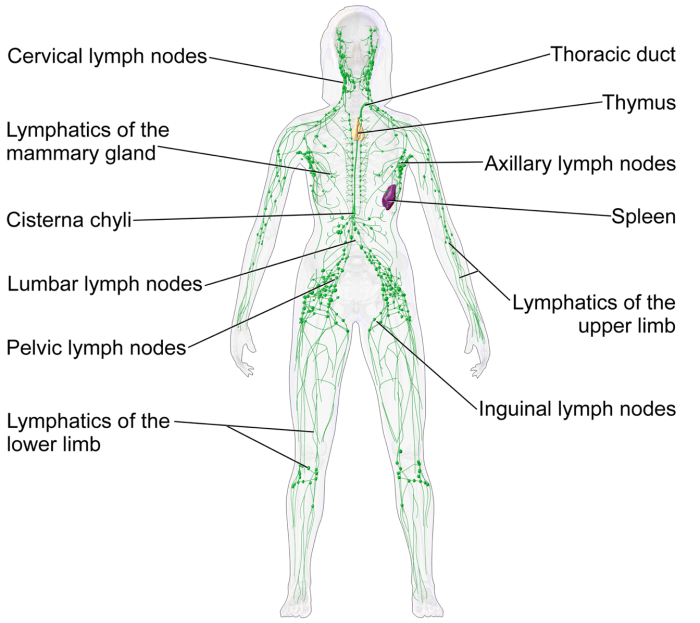
Lymph nodes are located throughout the body and are connected by lymphatic vessels. They contain specialized immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes, which work together to filter lymph fluid and remove pathogens.
Structure and Function of Lymphatic Vessels
Lymphatic vessels are thin-walled vessels that collect and transport lymph fluid from tissues throughout the body.
Structure of lymphatic vessels:
- Lymphatic capillaries: Microscopic vessels that form a network in tissues and collect lymph fluid.
- Lymphatic collecting vessels: Larger vessels that collect lymph fluid from lymphatic capillaries and transport it to lymph nodes.
Function of lymphatic vessels:
- Lymphatic capillaries: Collect excess fluid, proteins, and waste products from tissues.
- Lymphatic collecting vessels: Transport lymph fluid to lymph nodes for filtration and immune surveillance.
Lymphoid Organs and Tissues
Lymphoid organs and tissues are specialized structures that play a crucial role in the immune response.
Primary lymphoid organs:
- Thymus: Produces T lymphocytes, which are essential for cell-mediated immunity.
- Bone marrow: Produces B lymphocytes, which are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity.
Secondary lymphoid organs:
- Spleen: Filters blood and removes pathogens, and contains immune cells that can activate lymphocytes.
- Lymph nodes: Filter lymph fluid and contain immune cells that can activate lymphocytes and initiate immune responses.
Lymphoid tissues:
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT): Immune tissue located in the mucous membranes of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital tracts.
- Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): Immune tissue located in the digestive tract, including the Peyer’s patches.
Lymphocyte Circulation and Activation, Lymphatic system test questions and answers pdf
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune response.
Circulation of lymphocytes:
- Lymphocytes circulate through the lymphatic system and bloodstream, continuously monitoring for pathogens.
- When a pathogen is detected, lymphocytes migrate to the lymph nodes or other lymphoid tissues for activation.
Lymphocyte activation:
- Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) display antigens on their surface, which are recognized by lymphocytes.
- Recognition of an antigen triggers lymphocyte activation, leading to proliferation and differentiation into effector cells.
Edema and Lymphatic Drainage
Edema is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in tissues.
Causes of edema:
- Increased capillary permeability: Damage to capillary walls can lead to fluid leakage into tissues.
- Reduced lymphatic drainage: Blockage or dysfunction of lymphatic vessels can impair fluid removal.
- Increased hydrostatic pressure: Elevated pressure in the blood vessels can force fluid into tissues.
Role of the lymphatic system in edema reduction:
- The lymphatic system collects excess fluid from tissues and returns it to the bloodstream.
- Lymphatic drainage therapy can help reduce edema by stimulating the flow of lymph fluid.
Treatment options for edema:
- Elevation: Elevating the affected limb can help reduce hydrostatic pressure and promote fluid drainage.
- Compression therapy: Applying compression garments can help reduce edema by increasing pressure in the tissues and promoting lymphatic drainage.
- Lymphatic drainage therapy: Manual or mechanical techniques that stimulate the flow of lymph fluid.
Clinical Applications
Common lymphatic system disorders:
- Lymphedema: Chronic swelling caused by impaired lymphatic drainage.
- Lymphoma: Cancer of the lymphatic system.
Diagnostic tests used to evaluate lymphatic function:
- Lymphoscintigraphy: A nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses a radioactive tracer to visualize the lymphatic system.
- Lymphangiography: An X-ray imaging technique that uses a contrast agent to visualize lymphatic vessels.
Principles of lymphatic drainage therapy:
- Manual lymphatic drainage: A gentle massage technique that stimulates the flow of lymph fluid.
- Mechanical lymphatic drainage: The use of devices to apply pressure and stimulate lymphatic drainage.
FAQ Guide
What are the main functions of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in fluid drainage, immune responses, and fat absorption.
What is the role of lymph nodes in the lymphatic system?
Lymph nodes act as filters, trapping and eliminating harmful substances and pathogens from the lymph.
What are the different types of lymphoid tissues?
Lymphoid tissues include primary lymphoid organs (thymus, bone marrow) and secondary lymphoid organs (spleen, lymph nodes), as well as diffuse lymphoid tissues (MALT, GALT).