Introducing the solutions acids and bases portfolio, a comprehensive resource that delves into the fascinating world of acids, bases, and their interactions in solutions. This portfolio offers a captivating journey through the fundamental concepts, properties, and applications of these essential chemical components, providing a solid foundation for understanding their significance in various scientific disciplines.
Acids and bases, the cornerstone of chemistry, play a crucial role in shaping our world. From the acidic nature of lemon juice to the basic properties of household cleaning agents, these substances are ubiquitous in our daily lives. Understanding their behavior in solutions is paramount to unraveling the complexities of chemical reactions and processes.
Acids and Bases: A Comprehensive Overview
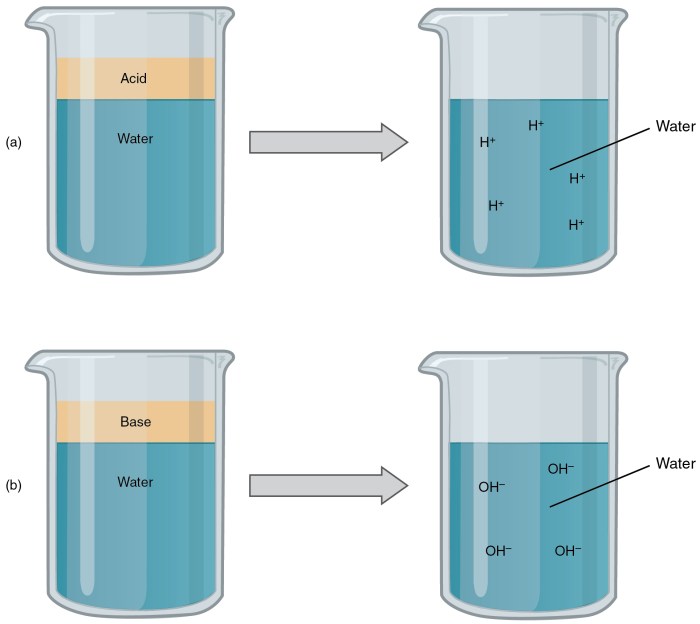
Acids and bases are fundamental concepts in chemistry, describing substances that exhibit characteristic properties and undergo specific reactions. They play a crucial role in various natural and industrial processes, contributing to our understanding of chemical behavior and the interactions between substances.
Definitions of Acids and Bases
Over time, different definitions of acids and bases have emerged, each providing a distinct perspective on their properties and behavior. Three widely recognized definitions include:
- Arrhenius Definition:Acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while bases produce hydroxide ions (OH-).
- Brønsted-Lowry Definition:Acids are substances that donate protons (H+), and bases are substances that accept protons.
- Lewis Definition:Acids are electron-pair acceptors, and bases are electron-pair donors.
These definitions highlight the fundamental characteristics of acids and bases, enabling us to classify and understand their chemical behavior.
Solutions
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more chemical substances. The substance present in the largest amount is called the solvent, while the substance present in the smaller amount is called the solute. The concentration of a solution is a measure of the amount of solute present in a given amount of solvent.
Solutions can be classified into two types: homogeneous and heterogeneous. Homogeneous solutions are those in which the solute is evenly distributed throughout the solvent. Heterogeneous solutions are those in which the solute is not evenly distributed throughout the solvent. Instead, the solute may be present as a separate phase, such as a solid or liquid, suspended in the solvent.
The behavior of a solution is affected by a number of factors, including temperature, pressure, and solvent polarity. Temperature affects the solubility of the solute in the solvent. Generally, the solubility of a solute increases with increasing temperature. Pressure affects the solubility of gases in liquids.
Generally, the solubility of a gas in a liquid increases with increasing pressure.
Factors Affecting Solution Behavior
- Temperature:The solubility of a solute in a solvent generally increases with increasing temperature. This is because the higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy the molecules have, and the more likely they are to overcome the intermolecular forces that hold them together.
- Pressure:The solubility of a gas in a liquid increases with increasing pressure. This is because the higher the pressure, the more gas molecules are forced into the liquid.
- Solvent polarity:The polarity of a solvent affects the solubility of solutes. Polar solvents are able to dissolve polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents are able to dissolve nonpolar solutes. Like dissolves like.
Acid-Base Equilibria
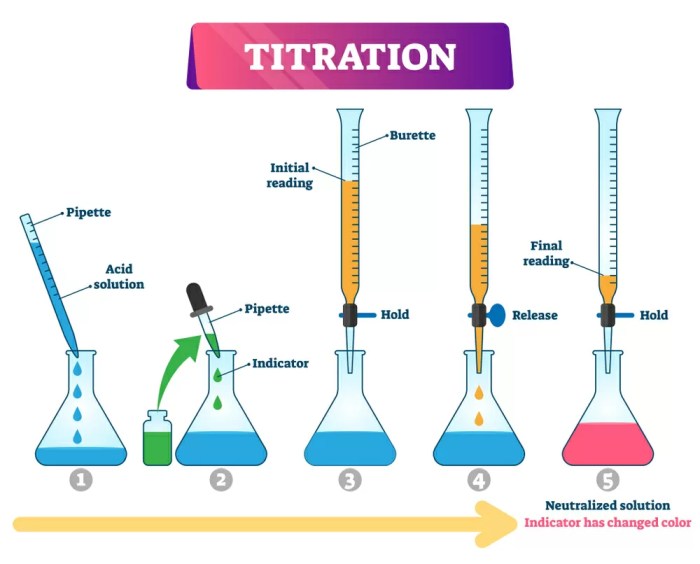
Acid-base equilibria are dynamic processes in which acids and bases react to form conjugate acid-base pairs. These equilibria play a crucial role in various chemical systems, including biological processes, environmental chemistry, and industrial applications.
The extent of an acid-base reaction is governed by the equilibrium constant (K eq). K eqis a quantitative measure of the relative concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. A large K eqindicates that the reaction proceeds predominantly towards product formation, while a small K eqsuggests that the reactants are favored.
Factors Affecting Acid-Base Equilibria
Several factors can influence the position of acid-base equilibria, including:
- Temperature:Increasing temperature generally shifts the equilibrium towards the endothermic side of the reaction. For exothermic reactions, increasing temperature shifts the equilibrium towards the reactant side.
- Solvent:The nature of the solvent can affect the strength of acids and bases. Polar solvents, such as water, favor the dissociation of ionic compounds, while nonpolar solvents promote the formation of covalent bonds.
- Ionic Strength:The presence of other ions in the solution can influence the equilibrium position. High ionic strength can decrease the activity of ions, leading to a shift in the equilibrium towards the side with fewer ions.
Applications of Acids and Bases in Various Fields
Acids and bases play a vital role in numerous industries and scientific disciplines, including manufacturing, medicine, and environmental science. Their applications range from acid-base titrations and pH control to chemical synthesis and environmental remediation. Understanding acid-base chemistry is crucial for professionals in these fields to optimize processes, ensure product quality, and safeguard human health and the environment.
Manufacturing
- Acid-Base Titrations:Used to determine the concentration of unknown acids or bases by neutralizing them with a solution of known concentration.
- pH Control:Maintaining the desired pH in industrial processes, such as food processing, textile manufacturing, and water treatment, is essential for optimal product quality and efficiency.
- Chemical Synthesis:Acids and bases are used as catalysts or reagents in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, plastics, and fertilizers.
Medicine
- pH Regulation:Maintaining proper pH levels in the body is crucial for various physiological processes, including enzyme function and nutrient absorption.
- Acid-Base Balance:Monitoring and regulating the acid-base balance in blood and other body fluids is essential for maintaining homeostasis and preventing life-threatening conditions.
- Drug Development:Acids and bases are used in the design and synthesis of new drugs, as well as in drug delivery systems to control the release and absorption of medications.
Environmental Science, Solutions acids and bases portfolio
- pH Control in Water Bodies:Acids and bases are used to adjust the pH of lakes, rivers, and wastewater to support aquatic life and prevent environmental damage.
- Acid Rain Mitigation:Neutralizing the acidity of rain using alkaline compounds helps reduce its harmful effects on ecosystems and infrastructure.
- Environmental Remediation:Acids and bases are employed in soil remediation to neutralize contaminants and restore soil health.
FAQ Explained: Solutions Acids And Bases Portfolio
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) in solution, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-).
What is pH?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 indicates a neutral solution, while values below 7 indicate acidic solutions and values above 7 indicate basic solutions.
What are some common applications of acids and bases?
Acids and bases have numerous applications in various industries, including manufacturing, medicine, and environmental science. For example, acids are used in batteries, fertilizers, and metalworking, while bases are used in detergents, soaps, and pharmaceuticals.